Language Transfer of Mandarin on English Phonetics Learning
#Language Transfer, #Second Language Learning
#Phonetics and Phonology, #Techonology for K-12 Education
Duration: 6 months, Jan 2018 - Jun 2018
Language transfer refers to the influence of previously learned language on target language, due to their similarities and differences. Lado (1957) first put forward the term “language transfer” based on the theory of behaviorism: Individuals tend to transfer the forms and meanings of their native language to the foreign language both productively and receptively.
Chinese language belongs to Sino-Tibetan phylum, and English belongs to Indo-European phylum, and have many differences that may potentially influence ESL learners’ phonetics acquisition.

In recent years, attentions have been increasingly drawn to the phenomenon of language transfer and the research focus shifting from segmental phonemes to suprasegmental phonemes. In my thesis I investigates Chinese language transfer on both segmental level and suprasegmental level on English phonetics. Research method chosen was acoustic experiment and experiment subjects were thirty-nine students in Grade seven, in Songbai Junior high school, Xiamen. The speech analysis software Praat was used in the speech visualization and analysis.
Research finding shows on the segmental level, student perform significantly better in English diphthong, possibly correlated with positive transfer from Chinese language, as many diphthong have same or similar phonemes in Chinese. Students’ performance on monophthong and consonants that do not exist in the Chinese language system was relatively worse, which could be explained by the negative language transfer theory.
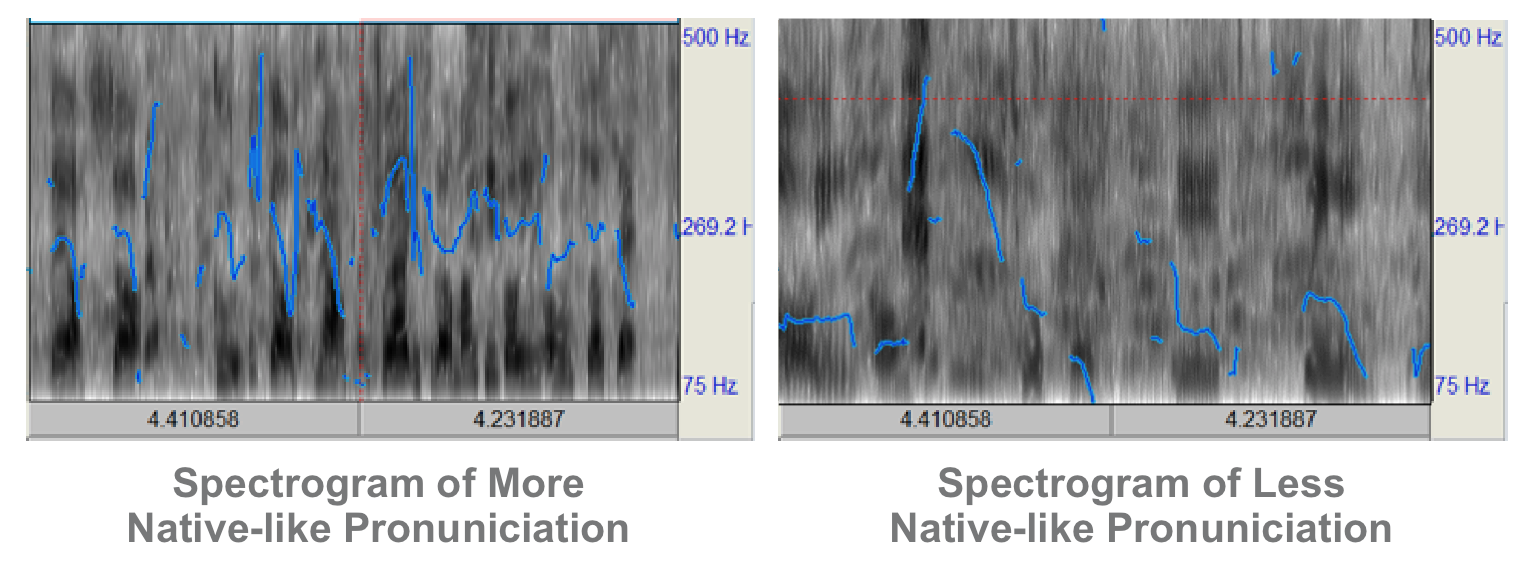
On the suprasegmental level, students have features of pronouncing too hastily, neglecting the pauses, rhythm and stress, reading English in a staccato instead of legato way.
This paper suggests future teachers to make use of tools and software such as Praat for educational purposes, to provide corrective feedback for students’ pronunciation. This computer-assisted pedagogy for English phonetics may help learners more easily assess and monitor their pronunciation by visualizing the pitch and spectrogram of their pronunciation.
